Outline
How to Build a Financial Model?
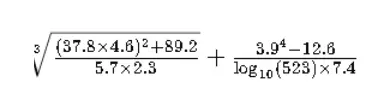
Can you solve this equation without using a scientific calculator?
Unless you are Shakuntala Devi or some other mathematical genius, it is a bit difficult to do it without using any tool! Similarly for projecting a company’s financial future via fundamental analysis, one needs a grasp on Financial Models.
Outline
This article demystifies the step-by-step guide to building financial models.
But first thing first, let’s understand what a financial model is.
What is Financial Modeling?
Financial models are the toolkit that aids in forecasting a company’s future.
By inputting past and present data into these models, we get a window to the future performance of the company which proves helpful in decision-making. Financial models are based on accounting principles, so a grasp of them is a must.
They act as financial machines, and learning to operate them is a must for anyone who wants to project revenues, cash flows, and other important indicators.
While creating accurate models can be challenging, the benefits are immense—which is what we are going to cover in the next section.
Benefits of Financial Models
- Direction and Insight: It is like a roadmap that h1.elps in identifying key business drivers, and potential risks, and helps in mitigating those risks effectively.
- Investor Confidence: A robust financial model showcases the modeler’s confidence and rational thinking. It provides a basis for company valuation which instills confidence in investors.
- Improved Decision-Making: These models translate real-world complex scenarios into numerical representations that facilitate financial planning and strategic decision-making.
- Communication Tool: They aid in conveying abstract ideas into tangible proposals. Whether it’s explaining depreciation on assets or conducting sensitivity analyses, financial models break complex chunks of financial data into digestible pieces.
- Versatility: Financial Modelling is a versatile skill that applies to varied domains, right from corporate finance, and private equity to investment banking; mastering which can meaningfully contribute to decision-making processes.
- Assessing Project Viability: For investors, these models are useful in evaluating investment opportunities and determining the feasibility of the projects.
Financial modeling is a vital skill for anyone seeking a career in finance, and this step-by-step guide will help you understand how to create a financial model.
How to Build a Financial Model?
Here is a step-by-step guide to building a financial model-
1. Why do you want to build a financial model?
When you build a financial model, first decide why you’re doing it. This helps you to understand what data you require, what assumptions you are supposed to take-
Okay so there are two steps to be followed to answer the above-mentioned question-
First, what are you expecting to achieve from building the model? Do you wish to project expenses? Or do you want to forecast sales instead? What exactly is your purpose?
Second, Look at the existing models and adjust them as per your requirements. But first figure out why, or else the outcome would be far from appropriate predictions.
2. Now decide what’s going to be the approach to building the financial model
There are mainly two approaches to follow here-
Top Down:
- Envision the Bigger Picture and apply reverse engineering.
- Define the stepping stones that you need to cross before reaching the final destination.
- Calculate revenue first, then related costs, and so on.
Bottom Up:
- Begin with basic assumptions like sales, salespeople, other expenses, etc.
- Build your model based on these assumptions.
- Create scenarios to see how these variations (like hiring more salespeople) affect goals.
So, which one is right for you?
- Top-down can be subjective and overly optimistic, yet it can give better insights into milestones.
- However, Bottom-up offers a more structured and realistic perspective to these models.
- A balanced combination of both approaches can give a 360-degree overview of the analysis.
3. Start Gathering Data
Once you’re done with the above two steps, i.e. what is the purpose and approach for your financial model going to be, next get your hands on gathering data from financial statements, surveys, and market research.
Say if the purpose of your model is to forecast an entity’s revenue, then you require its historical FS, economy indicators, market trends, and industry reports.
Once the data collection process is over, input them into the model and start building formulas.
4. Selection of Inputs and Outputs
The next step in line is to understand the inputs that go into the model and the outputs expected from it. Assumptions and inputs like sales growth, capital expenditure, and interest rates are the inputs of the financial model, while profitability, cash flow, and return on investment go into the output section.
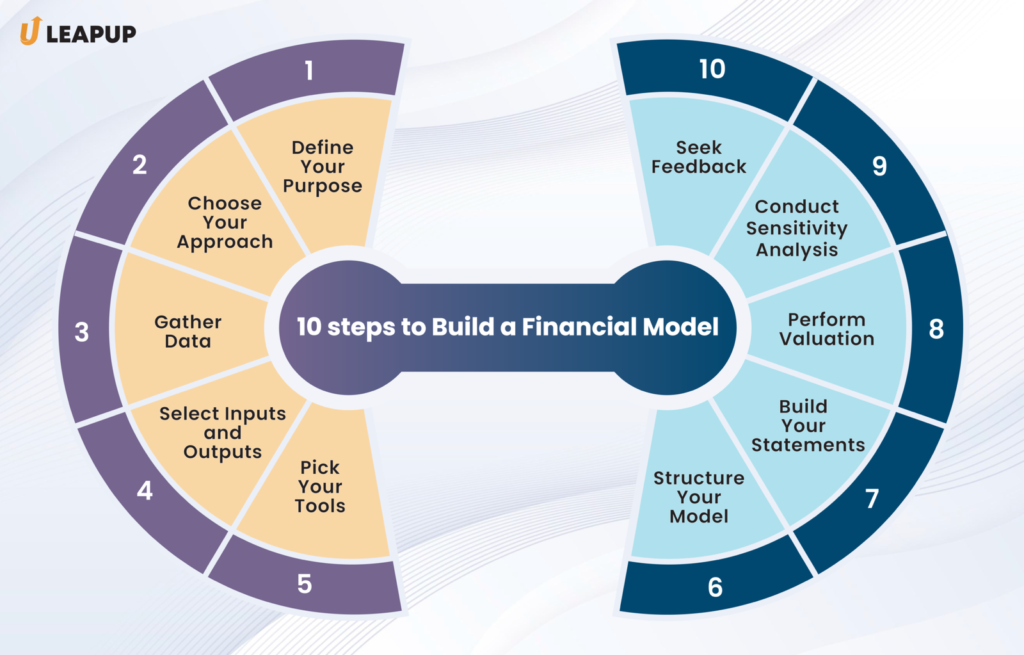
How to build a financial model?
Feel free to use this image by giving us an attribution link
5. Which application is suitable for building a financial model?
Financial modeling software varies in complexity and features. There are many options available, so you can pick one that suits your needs.
For beginners, a simple and widely used option like Microsoft Excel is a good choice. It doesn’t require much technical knowledge and is widely used in the industry.
If you need more advanced features, apps like Crystal Reports or Tableau offer greater functionality, but they are a little complex to adapt.
6. What are the Main Elements of a Financial Model?
A financial model consists of two main parts:
Assumptions (input) and Financial Statements (output), including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Additional elements like capital allocation, valuation, and sensitivity analysis can also be included based on the company’s needs. Let’s break down each part:
Assumptions and Drivers:
- This is the foundation of the financial model, containing variables used throughout.
- Assumptions are specific to each company, covering aspects like revenue growth, costs, and capital. They should be well-researched and reasonable, and not some blindly googled industry average.
- Supporting schedules, such as debt amortization schedules, can be included.
The Income Statement:
- The income statement showcases revenue and expenses. The main usage of this statement is to determine whether a company is profitable or not.
- This statement is bifurcated into operating and non-operating sections; for instance, revenue from property sales is non-operating for a software company.
- Provides insights into growth forecasts, margins, and cost-revenue relationships.
- Detailing into the Income Statement can be done with sub-categories relevant to the business entity.
The Balance Sheet:
- The balance sheet presents a snapshot of an entity’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- It reflects the financial health by showing what the company owns and owes.
- Balance sheet plays a pivotal role for startups mainly to track their net working capital balance, especially in the early stages, where they are making losses.
- Sales and net income figures from the income statement translate to assets and equity in the balance sheet.
The Cash Flow Statement:
- A cash flow statement is essential for understanding the movement of cash in a business.
- A key metric- Free Cash Flow indicates an entity’s ability to sustain its operations.
- This statement is built from the Income statement and balance sheet and has three components- Operational cash flow activities, financing activities, and investing activities.
- Investors are more interested in understanding how a company manages its cash, and this is where a cash flow statement comes into play.
7. Perform Valuation and Analysis, Check for Errors
After completing the three financial statements, it’s time to delve into valuation and sensitivity analysis to refine your financial model.
Discounted Cash Flow Analysis
With the groundwork laid by the financial statements, we initiate a discounted cash flow analysis. This involves estimating the free cash flow and then discounting it to present value using either the opportunity cost or the required rate of return. This initial step provides an initial valuation of the company.
There are other methods of valuation, which we can avail to perform this step, such as Market value, asset-based, etc.
Learn more about different types of business valuation methodologies here.
Assess Risk with Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis becomes crucial at this stage. By adjusting assumptions and exploring different operating scenarios, we can gauge how changes affect the company’s valuation.
But first, understand the concept of sensitivity analysis-
What is Sensitivity Analysis?
Sensitivity analysis is a fundamental technique within financial modeling, aimed at evaluating the impact of altering assumptions on a company’s financial performance. It allows for the identification of critical assumptions and their potential influence on financial outcomes.
Test the model’s sensitivity to changes in assumptions, such as varying interest rates or growth rates, to observe their impact on results.
This exercise helps in understanding and planning for potential risks, such as fluctuations in sales or unexpected shifts in marketing conversions.
Check for Errors: Ensure model accuracy by thoroughly examining for mistakes or formula discrepancies, commonly overlooked errors in financial modeling.
Simplify Your Model: Enhance usability by simplifying complex models. A simplified structure aids in comprehension and usability, facilitating effective decision-making processes.
8. Take Feedback, Adopt Best Practices
Before finalizing your financial model, it’s beneficial to seek feedback from others. Feedback can help identify errors and areas for improvement. As a financial analyst, sharing your model with colleagues, clients, or supervisors is common practice, emphasizing the importance of clarity and usability. You can also leverage LinkedIn to gather feedback on your model by connecting with relevant parties.
What are the signs of a Good Financial Model?
A well-constructed financial model exhibits specific features that enhance its effectiveness-
- A good financial model is logically structured and enables easy navigation.
- It has a clean and simple layout that facilitates better understanding.
- Has presented assumptions and forecast drivers for improved comprehension.
- In a well-built financial model, key fiscal concerns are appropriately emphasized that are relevant to shareholders.
- It incorporates visual aids like charts and graphs to present data visually, aiding in concept clarification.
Adheres to precision and reliability in the calculation.

How to build a financial model?
Feel free to use this image by giving us an attribution link
As much it is required to build a good financial model, it is equally important to communicate it with the relevant parties with effective model communication techniques, a few of which are listed below:
- Simple and concise language goes a long way in enhancing model communication.
- Leverage effective formatting techniques to emphasize crucial information and guide readers through the model.
- Include a detailed description outlining the model’s purpose, overview, and functionality.
Provide clear instructions for utilizing the model, ensuring ease of use for stakeholders.
Bottom Line!
Conclusively, building a financial model isn’t scary if you walk one step at a time. However, it is essential to plan strategically and know why you want to build a model. This can save you from having to make big changes later on. While using templates can be helpful to start with, it’s better to create your model from scratch to understand your business’s needs. This shows that you know your business well and can impress potential investors, which could help you get funding.
Enroll in the Best Financial Modeling and Valuation course-
Do you run a business, an investor, or a finance enthusiast willing to learn valuations but is scared to start? Enroll in our Comprehensive Financial Modelling and Valuations Course that covers all nitty gritties. It’s designed to help you feel confident in analyzing finances and making smart decisions.
Don’t believe us? See what our students have to say-




